3D Scanning & Reverse Engineering
What is 3D scanning?
3D scanning involves collecting point data, commonly referred to as point clouds, using specialized technologies such as structured light, infrared, or lasers. Once the data is collected, it is converted into a mesh. This mesh can be exported as either an STL or OBJ file. After importing the mesh into your preferred software or slicer, you have the option to 3D print the file yourself or outsource the printing process to someone who has the necessary equipment.
Additionally, the mesh can be enhanced or modified using software like Maya, Blender, or Cinema 4D.
3D scanning is particularly useful for cosplay, replication, and reverse engineering, which we'll explore further next.

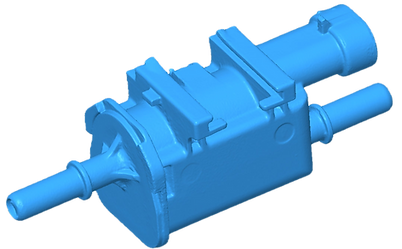
What is Reverse engineering?
Reverse engineering involves converting mesh data into a solid model that can be imported into a CAD system such as Fusion 360 or SolidWorks. However, it is important to note that these programs generally face challenges when handling high-density meshes, which can result in decreased performance or system crashes.
To address the challenge, utilizing specialized software that can accurately trace mesh data is an effective approach. This process allows for the creation of optimized solid bodies, facilitating further development. 3D scanning and reverse engineering present valuable opportunities for downstream applications by enabling users and companies to replicate obsolete parts that are no longer in production. Moreover, these techniques are invaluable for inspection, as they allow for a thorough comparison of scanned data with CAD data, ensuring quality and precision in manufacturing processes.against the CAD data.